Annual Report for National Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring (2019) Released
To fully reflect the status of China's adverse drug reaction (ADR) monitoring in 2019, improve the level of safe drug use, and better ensure drug safety for the public, the National Center for ADR Monitoring has organized the compilation of the Annual Report for National Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring (2019), which has been released on April 10, 2020.
Overall Situation of Adverse Drug Reaction Monitoring
In 2019, in accordance with General Secretary Xi Jinping's Four Strictest requirements for food and drugs, the monitoring and evaluation of adverse drug reactions (ADR) has been carried out steadily and orderly, the corresponding laws and regulations have been continuously improved, the monitoring & evaluation system has gradually become robust, the quantity and quality of case reports saw an upward trend, risk control measures have become more sophisticated, and remarkable results have been achieved in relevant fields, providing strong support for drug administration.
First of all, the information system has been improved to further lay a solid foundation for monitoring and evaluation. The national ADR monitoring network system has been improved. The monitoring system for drug Marketing Authorization Holders (hereinafter referred to as MAHs) to directly report ADRs has been officially in operation, effectively promoting the MAH's ADR monitoring. We continued to forge closer ties with medical institutions and explored new models for ADR monitoring. At present, we have established outposts for ADR monitoring in 189 Class-III medical institutions. In 2019, 97.4 percent of county-level regions across the country reported adverse drug reactions/events (ADR/ADE). The average number of reports per million populations in China reached 1,130, which laid a solid foundation for the in-depth development of monitoring and evaluation.
Secondly, scientific evaluation is reinforced to timely deal with risk warning signals. We established and improved the working mechanism of daily monitoring, weekly summarization and quarterly analysis. At the same time, we paid close attention to the domestic and foreign regulatory dynamics in close integration with our actual clinical medication practice, and continuously strengthened the analysis and evaluation of the ADR report data. According to the evaluation outputs, we timely released pharmacovigilance information. In 2019, we issued the Announcement on the Cessation of Production, Sale and Use of FurazolidoneContaining Compound Preparations, as well as 27 Announcements on the revision of drug package inserts, and 12 volumes ofPharmacovigilance Express. The functions of the early warning management platform were further optimized to realize early detection, response, investigation, and disposal of early warning signals to ensure effective protection of drug safety for the public.
Thirdly, the construction of standards is strengthened, and the transformation and implementation of ICH related guidance is promoted. The Guidance for Clinical Safety Literature Evaluation of Marketed Drugs (Interim) and Guidance for Compiling the Annual Pharmacovigilance Report by Marketing Authorization Holders (Interim) were issued to guide MAHs in monitoring, reporting, analysis and evaluation. We steadily promoted the transformation and implementation of E2B (R3: Clinical Safety Data Management - Data Elements for Transmission of Individual Case Safety Reports) of ICH (International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use), and released the Regional Implementation Guidance for Individual Case Safety Reports E2B(R3). We promoted the application of the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA), carried out disease term mapping research, strengthened the training for MAHs and monitoring institutions, and provided technical guarantee for full swing of ICH related Guidance.
Fourthly, we actively promoted publicity and guidance over ADRs to beef up public awareness. The 7th China Pharmacovigilance Conference was held to promote academic exchange and experience sharing in this field. We organized training for ADR monitoring to guide MAHs to implement their principal responsibility for drug safety, and raise their awareness for risk management. We've made full use of the National Safe Medicine Monthly Platform, as well as the internet, TV, newspapers and other media to actively disseminate the knowledge of adverse drug reactions; carried out various forms of activities such as public open days and joint urban-rural efforts, sparing no effort to increase public awareness of ADRs.
Status of ADR / ADE reporting
(I) Overview of reporting
The report of ADRs/ADEs in 2019
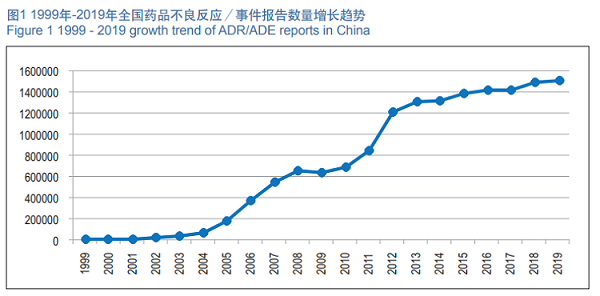
In 2019, the National ADR Monitoring Network received 1.514 million copies of ADR/ADE Report Form. From 1999 to 2019, the National ADR Monitoring Network received an accumulative total of 15.19 million copies of the ADR/ADE Report Form (See Figure 1).
2. New and serious ADR/ADE reporting
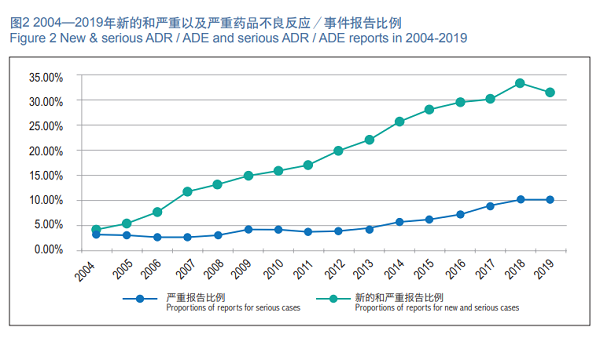
In 2019, the National ADR Monitoring Network received 477,000 new and serious ADR/ADE reports, accounting for 31.5 percent of the total number reported in the same period.
In 2019, the National ADR Monitoring Network received 156,000 reports of reports serious adverse drug reactions/incidents, and serious ADR/ADE reports accounted for 10.3 percent of the total reports for the same period (Figure 2).
3. Average case report per million population
The average number of reports per million population constitutes one of the major indicators to measure the level of a country's ADR monitoring work. The average number of reports per million population in China marked 1,130 in 2019.
4. Proportion of ADR/ADE reports at county level *
The ratio of ADR/ADE reports at county level constitutes one of the important indicators to measure the balanced development and coverage of ADR monitoring in China. In 2019, 97.4 percent of county-level regions across China reported ADRs/ADEs.
5. Sources of ADR/ADE reports
MAHs, pharmaceutical distributors and medical institutions constitute the responsible units for ADR / ADE reporting. As per source-specific statistics of ADR/ADE reports in 2019, a lion's share of 88.1 percent came from medical institutions; while a share of 6.6 percent, 5.2 percent, and 0.1 percent came from pharmaceutical distributors, MAHs, individuals and other sources, respectively (Figure 3).
6. Occupations of reporters
In occupation-specific statistics, of all the reporters, doctors accounted for 56.6%, pharmacists accounted for 22.3 percent, nurses accounted for 15.3 percent, and other occupations accounted for 5.8%.
7. Patients involved in the ADR/ ADE reports
In the 2019 ADR/ADE reports, the ratio of male to female patients was 0.86:1, with men slightly outnumbered by women. Reports of pediatric patients under 14 years of age accounted for 10.2 percent; and reports of elderly patients over 65 accounted for 29.1 percent.
8. Distribution of drug categories involved in 2019 ADR/ADE reports
As per category-specific statistics of suspected drugs, reports of chemical drugs, TCM and bio-products accounted for 84.9 percent, 12.7 percent and 1.6 percent, respectively, while 0.8 percent of the drugs are not classifiable.
As per the statistics of routes of administration of drugs involved in 2019 ADR/ADE reports, 62.8 percent were administered by injection, 32.5 percent by oral administration, and 4.7 percent by other routes of administration. Among injection administrations, intravenous administration accounts for 92.5 percent and other injection administrations account for 7.5 percent.
9. Systems damaged by ADRs/ADEs
Among the ADRs/ADEs reported in 2019, the top 5 organ system damages are: skin and its appendages damage; gastrointestinal damage; systemic damage, neurological impairment and cardiovascular system damage.



